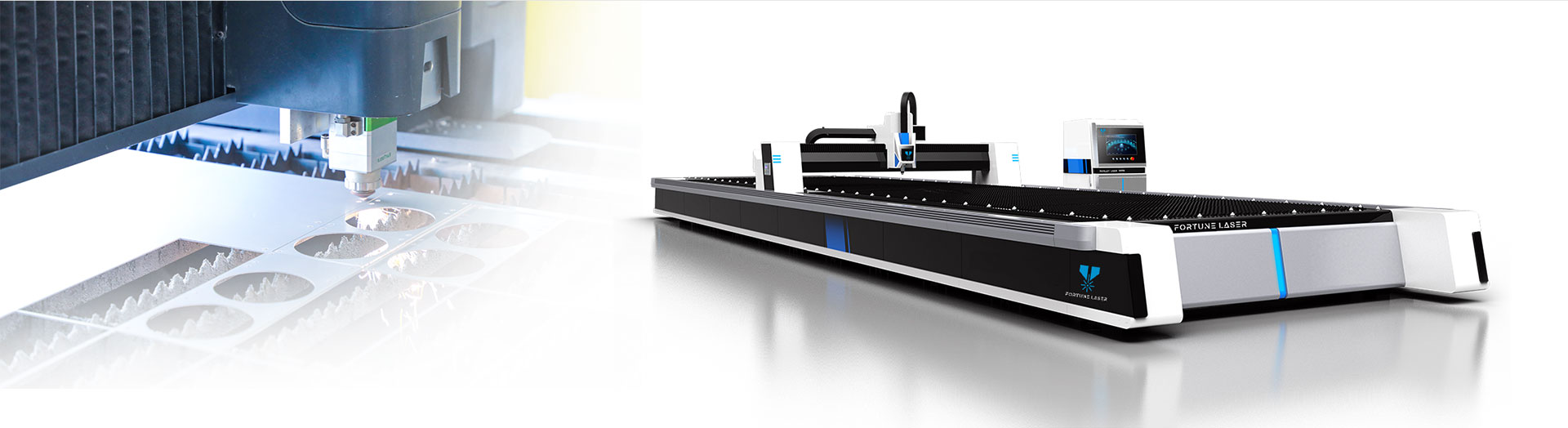
Laser cutting uses a focusing mirror to focus the laser beam on the surface of the material to melt the material. At the same time, the compressed gas coaxial with the laser beam is used to blow away the melted material and make the laser beam and the material move relative to each other along a certain trajectory, thereby forming a certain shape. Shaped slits.
Causes of overheating
1 material surface
Carbon steel will oxidize when exposed to air and develop an oxide scale or oxide film on the surface. If the thickness of this film/skin is uneven or it is raised and not close to the board, it will cause the board to absorb the laser unevenly and the heat generated will be unstable. This affects the ② step of the above cutting. Before cutting, try to place it with the side with the best surface condition facing up.
2 Heat accumulation
A good cutting state should be that the heat generated by the laser irradiation of the material and the heat generated by oxidative combustion can be effectively diffused to the surroundings and effectively cooled. If cooling is insufficient, overheating may occur.
When the processing trajectory involves multiple small-sized shapes, heat will continue to accumulate as the cutting progresses, and overburning can easily occur when the second half is cut.
The solution is to spread the processed graphics as much as possible so that the heat can be effectively dispersed.
3 Overheating at sharp corners
Carbon steel will oxidize when exposed to air and develop an oxide scale or oxide film on the surface. If the thickness of this film/skin is uneven or it is raised and not close to the board, it will cause the board to absorb the laser unevenly and the heat generated will be unstable. This affects the ② step of the above cutting. Before cutting, try to place it with the side with the best surface condition facing up.
Overburning of sharp corners is usually caused by heat build-up because the temperature of the sharp corners has risen to a very high level as the laser passes over it. If the forward speed of the laser beam is greater than the heat transfer speed, overburning can be effectively avoided.
How to solve overheating?
Under normal circumstances, the heat conduction speed during over-burning is 2m/min. When the cutting speed is greater than 2m/min, melting loss will basically not occur. Therefore, using high-power laser cutting can effectively prevent overburning.
Post time: Mar-22-2024