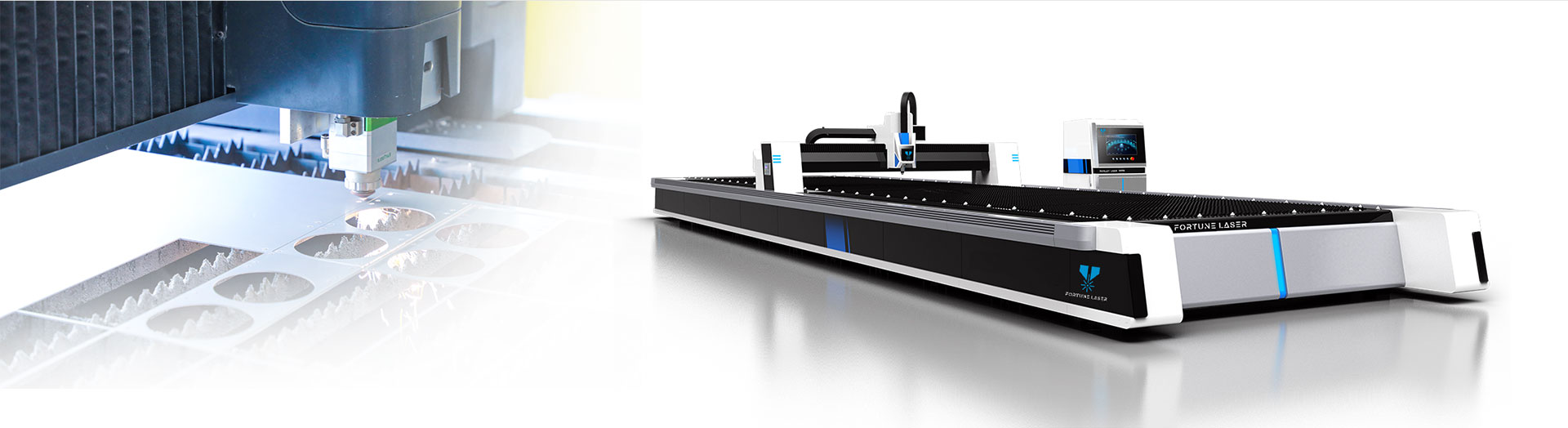
CNC precision laser cutting machines have revolutionized manufacturing with their ability to cut a variety of materials with unparalleled precision and efficiency. In terms of cutting materials and thickness, laser cutting machines can process a wide range of materials, including metals, non-metallic materials, textiles, and even stone. Different types of laser cutting machines, especially fiber lasers with different powers, have different capabilities and limitations when cutting materials of different thicknesses. In this article, we will explore the materials and thicknesses that CNC precision laser cutting machines can cut.
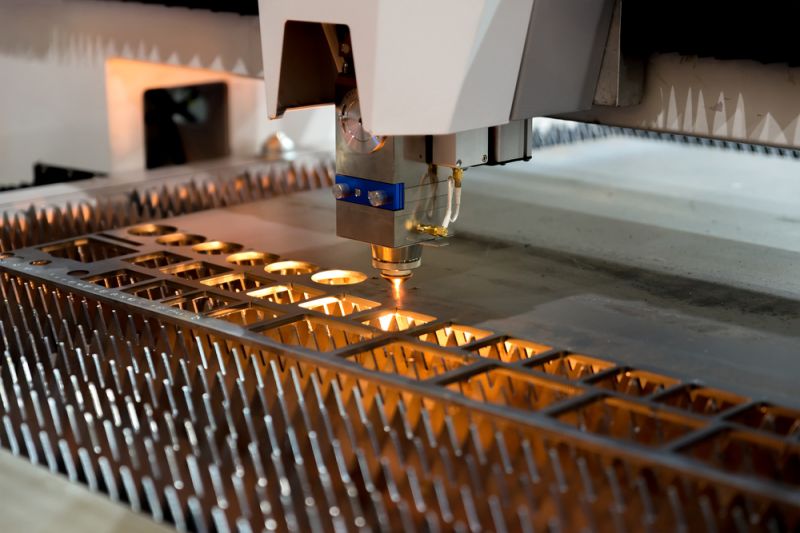
Metal materials such as steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys are the most commonly processed materials by laser cutting machines. The precision and versatility of laser cutting technology make it a valuable tool for the metal fabrication industry. Whether cutting intricate designs on stainless steel sheets or processing thick carbon steel plates, laser cutting machines are capable of handling a variety of metal materials and thicknesses. For example, the maximum cutting thickness of a 500W fiber laser cutting machine is 6mm for carbon steel, 3mm for stainless steel plates, and 2mm for aluminum plates. On the other hand, the 1000W fiber laser cutting machine can cut carbon steel up to 10 mm thick, stainless steel up to 5 mm thick, and aluminum plates up to 3 mm thick. The capability of the 6000W fiber laser cutting machine can be extended to cutting carbon steel up to 25 mm thick, stainless steel up to 20 mm thick, aluminum plates up to 16 mm thick, and copper plates up to 12 mm thick.
In addition to metal materials, CNC precision laser cutting machines can also cut non-metallic materials such as acrylic, glass, ceramics, rubber, and paper. These materials are commonly used in a variety of industries, including signage, decorative arts, packaging, and more. Laser cutters provide the precision and speed needed to cut and engrave complex designs on non-metallic materials, making them ideal for a variety of applications. In addition, textile materials such as cloth and leather can also be processed using laser cutting technology, allowing manufacturers to achieve clean and precise cuts of various textile products.
Laser cutters have also proven their capabilities when it comes to cutting stone materials such as marble and granite. The precision and power of laser cutting technology enable cutting of stone with complex designs and shapes, opening up new possibilities for architectural and decorative applications. The ability to cut stone using a laser cutter provides manufacturers with a more efficient and cost-effective solution compared to traditional cutting methods.
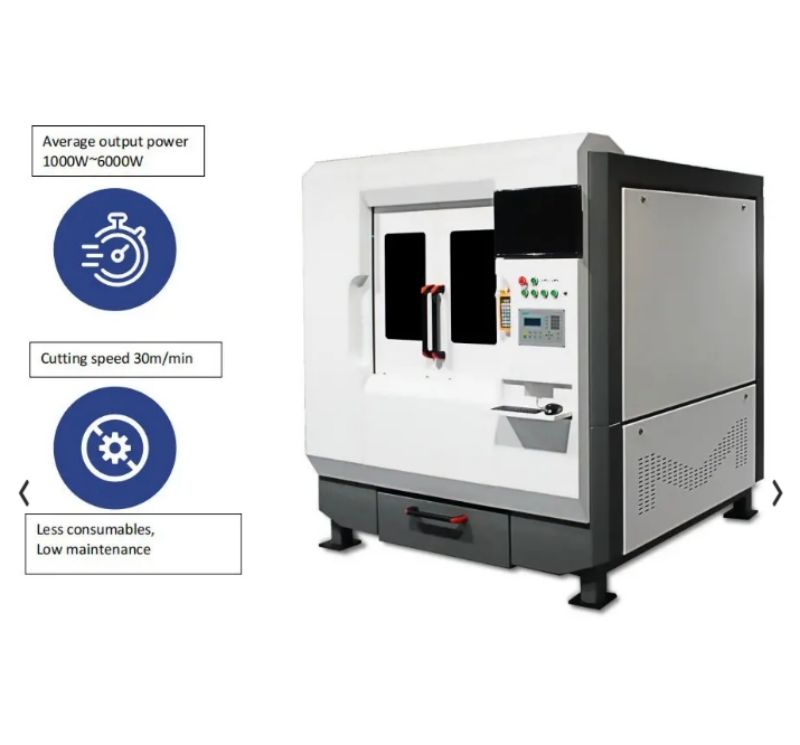
It is worth noting that the functionality of CNC precision laser cutting machines is highly dependent on the power of the laser source. Different types of fiber lasers with different power outputs provide different capabilities when cutting materials of different thicknesses. For example, a 500W fiber laser cutting machine is suitable for cutting thinner materials, while a 6000W fiber laser cutting machine is able to handle thicker and stronger materials. Manufacturers must consider the specific requirements of their project and select the right laser cutter with the right power output to achieve the desired results.
In summary, CNC precision laser cutting machines have excellent features when cutting materials of different thicknesses. With the ability to cut metal, non-metallic materials, textiles and even stone, laser cutting machines have become a staple in the manufacturing industry. Whether achieving precise cuts in thin stainless steel sheets or machining thick sheets of carbon steel, laser cutting machines deliver unparalleled precision and efficiency. The different power levels of fiber lasers also provide manufacturers with the flexibility to select the right machine for their specific application. As technology continues to advance, CNC precision laser cutting machines will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping the future of manufacturing in various industries.
Post time: Jan-18-2024